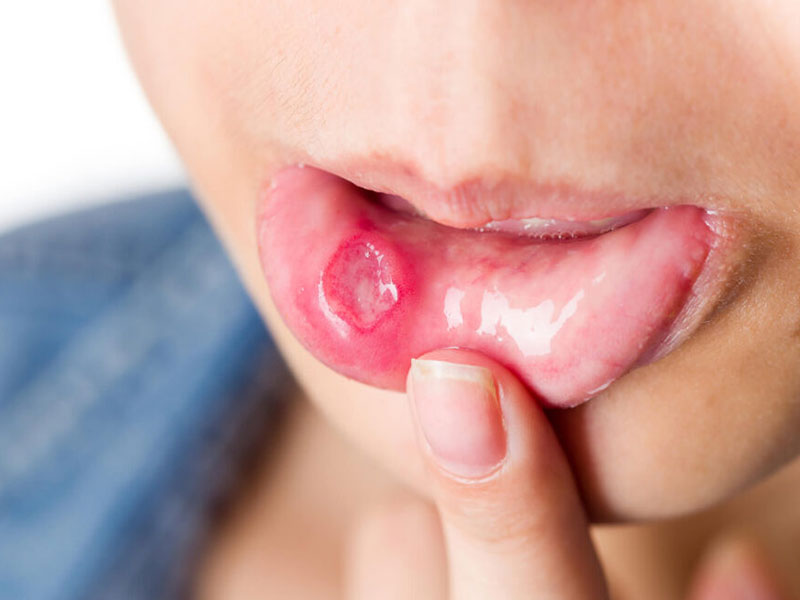
Oral cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that arises in the tissues of the mouth or throat. At Eva's Dental & Maxillofacial, Oral Cancer Center, we are dedicated to providing the highest quality care for individuals diagnosed with oral cancer. Led by Dr. Gideon Arularasan, an experienced Oral Surgeon with over 15 years of experience in Chennai, our center is equipped with the latest technology and expertise to diagnose and treat oral cancer effectively.
Understanding Oral Cancer
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, encompasses a range of cancers that affect various parts of the mouth and throat. This includes the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palate, sinuses, and pharynx. Like all cancers, oral cancer occurs when cells in these areas undergo abnormal changes and begin to grow uncontrollably.
Types of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer can manifest in several forms, each originating in different tissues of the mouth or throat. The most common types include:
1. Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
This is the most prevalent type of oral cancer, accounting for over 90% of cases. Squamous cells are flat, thin cells that line the mouth and throat. When these cells become malignant, they form squamous cell carcinoma, which can be aggressive and spread rapidly.
2. Verrucous Carcinoma:
A less common variant of squamous cell carcinoma, verrucous carcinoma is a slow-growing cancer that often appears as a wart-like growth in the mouth. While it is less likely to metastasize, it can invade surrounding tissues and requires prompt treatment.
3. Minor Salivary Gland Carcinomas:
These cancers arise in the minor salivary glands located throughout the lining of the mouth and throat. Examples include adenocarcinomas, adenoid cystic carcinomas, and mucoepidermoid carcinomas.
4. Lymphomas:
Lymphomas can occur in the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils or the base of the tongue. These cancers are part of a broader category known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
5. Melanomas:
Although rare, melanomas can develop in the mucous membranes of the mouth. Oral melanomas are aggressive and often present as dark, pigmented lesions.
Symptoms of Oral Cancer
The symptoms of oral cancer can vary depending on the type and location of the cancer. Early detection is crucial, so it is important to be aware of the following signs:
1. Persistent Mouth Sores:
A sore in the mouth that does not heal within two weeks can be an early sign of oral cancer.
2. Red or White Patches:
The presence of red or white patches on the gums, tongue, or lining of the mouth may indicate pre-cancerous changes.
3. Unexplained Bleeding:
Any unexplained bleeding in the mouth should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
4. Difficulty in Swallowing or Chewing:
Oral cancer can cause pain or a sensation of something being stuck in the throat, leading to difficulty in swallowing or chewing.
5. Numbness or Tingling:
A persistent numbness or tingling sensation in the mouth or lips can be a warning sign.
6. Changes in Voice:
Hoarseness or a change in voice that persists may be a symptom of throat cancer.
7. Ear Pain:
Chronic ear pain, particularly in one ear, without hearing loss, can be related to oral cancer.
8. Unexplained Weight Loss:
Sudden and unexplained weight loss may be a sign of an underlying health issue, including oral cancer.
Causes and Risk Factors of Oral Cancer
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with oral cancer can help in prevention and early detection. Several factors can increase the risk of developing oral cancer, including:
1. Tobacco Use:
The use of tobacco in any form—cigarettes, cigars, pipes, chewing tobacco, or snuff—is the leading cause of oral cancer. Tobacco users are at a significantly higher risk than non-users.
2. Alcohol Consumption:
Excessive alcohol consumption is another major risk factor. When combined with tobacco use, the risk increases dramatically.
3. Human Papillomavirus (HPV):
Certain strains of HPV, particularly HPV-16, have been linked to oropharyngeal cancers. The virus can cause changes in the cells of the mouth and throat, leading to cancer.
4. Sun Exposure:
Prolonged exposure to the sun without protection can increase the risk of cancer on the lips, particularly the lower lip.
5. Age:
The risk of oral cancer increases with age, with most cases occurring in individuals over the age of 40.
6. Poor Diet:
A diet low in fruits and vegetables may increase the risk of developing oral cancer. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants can help protect against cancer.
7. Family History:
A family history of cancer can increase an individual’s risk of developing oral cancer.
8. Gender:
Men are more likely than women to develop oral cancer, possibly due to higher rates of tobacco and alcohol use.
Prevention and Early Detection
Preventing oral cancer involves making lifestyle changes and being vigilant about oral health. Key preventive measures include:
1. Quitting Tobacco:
The single most effective way to reduce the risk of oral cancer is to quit using tobacco products.
2. Limiting Alcohol Intake:
Moderating alcohol consumption can significantly lower the risk of oral cancer.
3. HPV Vaccination:
Vaccination against HPV can reduce the risk of HPV-related oral cancers.
4. Regular Dental Check-ups:
Routine dental exams are crucial for early detection. Dentists can identify pre-cancerous changes and recommend appropriate interventions.
5. Protecting Lips from the Sun:
Using lip balm with SPF and wearing a wide-brimmed hat can protect the lips from harmful UV rays.
6. Maintaining a Healthy Diet:
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall health and reduce cancer risk.
Diagnosis and Treatment
At Eva's Dental & Maxillofacial, Oral Cancer Center, we offer comprehensive diagnostic services to accurately identify oral cancer. Our diagnostic process may include:
1. Physical Examination:
A thorough examination of the mouth, throat, and neck to identify any abnormalities.
2. Biopsy:
If a suspicious area is found, a biopsy may be performed to obtain a tissue sample for analysis.
3. Imaging Tests:
Advanced imaging techniques such as CT scans, MRI, and PET scans help determine the extent of the cancer and plan appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options
The treatment of oral cancer depends on the stage and location of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health. Common treatment options include:
1. Surgery:
Surgical removal of the cancerous tissue is often the first line of treatment. In some cases, this may involve removing part of the jawbone or tongue.
2. Radiation Therapy:
High-energy beams are used to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be used alone or in combination with surgery.
3. Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. It is often used in conjunction with radiation therapy.
4. Targeted Therapy:
Targeted therapy drugs work by targeting specific molecules involved in cancer growth. These drugs may be used in combination with other treatments.
5. Rehabilitation:
After treatment, rehabilitation may be necessary to restore function and appearance. This may include speech therapy, physical therapy, and reconstructive surgery.
Conclusion
Oral cancer is a serious condition, but with early detection and appropriate treatment, the chances of successful outcomes are significantly improved. At Eva's Dental & Maxillofacial, Oral Cancer Center in Chennai, we are committed to providing compassionate, expert care for our patients. If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above or have risk factors for oral cancer, we encourage you to schedule a consultation with Dr. Gideon Arularasan.